- System requirements
- Profiler architecture
- Profiler installation
- Uninstall profiler
- Running the profiler
- Profiler activation
- Welcome screen
- Start profiling
- Profiling overhead
- Snapshots
- Solving performance problems
- CPU profiling
- Thread profiling
- Virtual threads support
- Object allocation profiling
- Memory profiling
- Monitor profiling
- Exception profiling
- Telemetry
- Probes: monitor events of various kinds
- Inspections: automatic recognition of typical problems
- Automatically trigger actions on event
- Automatic deobfuscation
- Summary
- Filters
- Profiler command line
- Export of profiling results to external formats
- Profiler Java API
- Profiler HTTP API
- Settings
- Troubleshooting and FAQ
CPU hot spots
Hot spots shows methods that consumed the most time. The host spots list is similar to the method list sorted by time, but it excludes the methods which do not consume time itself. I.e if the time was consumed only in called methods, then the caller method is not a host spot. In other words the most important methods for application performance are shown.
Profiler shows hot spots in CPU tracing, sampling and asynchronous sampling modes. For call counting mode the list is not available, because call stacks are not collected.
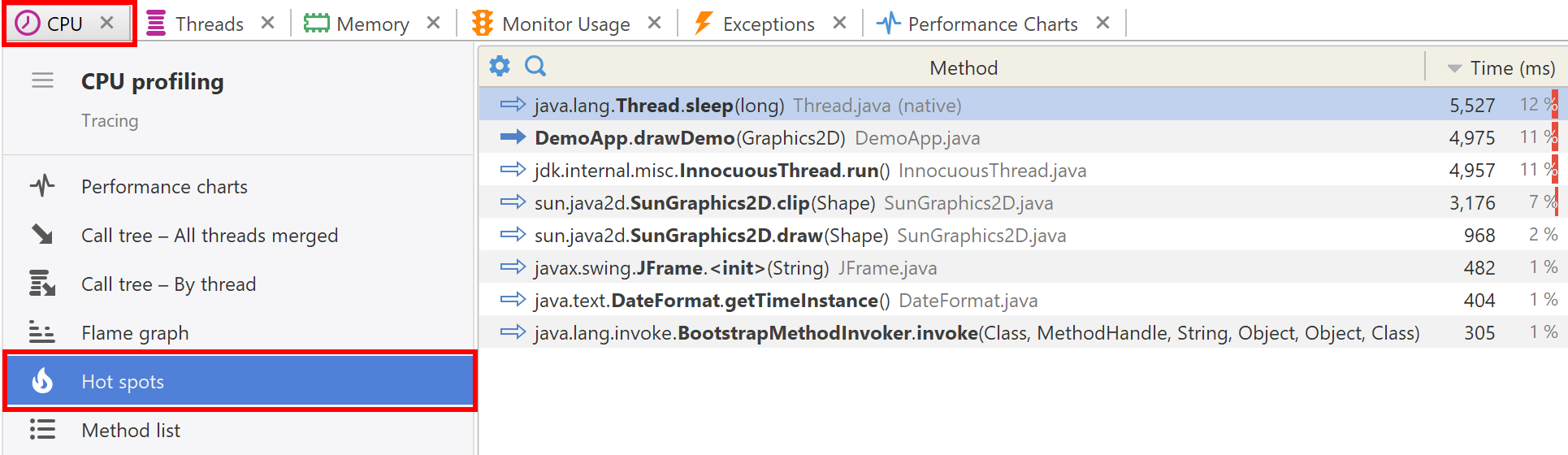
The hot spots are calculated based on current filters. Every time you change filters, you get the new list of hot spots.
Actions
The following actions are available in the popup menu:
- CPU | Method Merged Callees (Ctrl+M) - shows the method's merged callees.
- CPU | Method Back Traces (Ctrl+Shift+M) - shows the method's back traces.
- Tools | Open in IDE (F7) - opens method declaration in IDE editor. See IDE integration.
